Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
General
The Dynamic Cone Penetrometer (DCP) is used to measure the rate of penetration through the various layers of a pavement. In South Africa, the measurement of the in-situ shear strength of the pavement layers using a DCP, has also led to the development of pavement evaluation and rehabilitation design methods. The DCP component (layer by layer) analysis method is empirically derived based on material shear strength and can only be accurate if used for the evaluation and analysis of pavements similar to those from which they were derived.
It follows that the DCP test provides meaningful, but incomplete information about the expected behaviour of a pavement. Although in-situ material shear strength data are relatively complete with the DCP, if found applicable, it can give extremely good results and information about the future behaviour of a pavement. It follows that the key to the successful application of empirically derived methods based on CBR and/or DCP measurements lies in the applicability of the method to a specific pavement. It is, however, advised that the method be used in a multi-analysis approach together with other methods.
The figure below shows a schematic of the DCP.
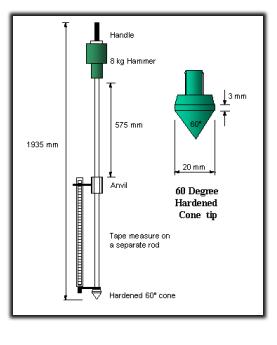
Conducting the test and collecting data
The DCP test is conducted by lifting and dropping the hammer onto the anvil, and measuring the penetration of the DCP cone into the pavement layers. Data are typically collected by measuring the penetration afetr each 5 blows, up to a total depth of 800 mm.
