Basic HMA weight-volume relationships are important to understand for both mix design and construction purposes. Fundamentally, mix design is meant to determine the volume of asphalt binder and aggregates necessary to produce a mixture with the desired properties (Roberts et al., 1996[1]). However, since weight measurements are typically much easier, they are typically taken then converted to volume by using specific gravities. The following is a brief discussion of the more important volume properties of HMA.
In general, weight and volume terms are abbreviated as, Gxy,
| where | x: | b | equals | binder |
| s | equals | stone (i.e., aggregate) | ||
| m | equals | mixture | ||
| y: | b | equals | bulk | |
| e | equals | effective | ||
| a | equals | apparent | ||
| m | equals | maximum | ||
For example, Gmm = gravity, mixture, maximum = the maximum gravity of the mixture. Other common abbreviations are:
| VT | equals | Total volume of the compacted specimen | WT | equals | Total weight of the compacted specimen |
| Va | equals | Volume of air voids | WD | equals | Dry weight |
| Vb | equals | Volume of asphalt binder | WSSD | equals | Saturated surface dry (SSD) weight |
| Vbe | equals | Volume of effective asphalt binder | Wsub | equals | Weight submerged in water |
| Vba | equals | Volume of absorbed asphalt binder | Wb | equals | Weight of the asphalt binder |
| Vagg | equals | Volume of aggregate | Wbe | equals | Weight of effective asphalt binder |
| Veff | equals | Effective volume of aggregate = (VT – VAC) | Wba | equals | Weight of absorbed asphalt binder |
| Wagg | equals | Weight of aggregate | |||
| Gsa | equals | Apparent specific gravity of the aggregate | |||
| Gb | equals | Asphalt binder specific gravity | Pb | equals | Asphalt content by weight of mix (percent) |
| Gsb | equals | Bulk specific gravity of the aggregate | Ps | equals | Aggregate content by weight of mix (percent) |
| Gse | equals | Effective specific gravity of the aggregate | Pa | equals | Percent air voids |
| Gmb | equals | Bulk specific gravity of the compacted mixture | |||
| Gmm | equals | Maximum theoretical specific gravity of the mixture | γW | equals | Unit weight of water |
HMA Constituents
In general, HMA is made up of 3 materials: aggregate, asphalt binder and air. Typically, HMA is described by volume so it is important to know how these 3 materials relate to one another volumetrically. The animation in Figure 1 shows this both in a close-up sketch of in-place HMA (left) and a volume diagram (right) that is similar to volume diagrams seen in the geotechnical arena. Further definitions of these terms can be found below.
Specific Gravities
Bulk Specific Gravity of the Compacted Asphalt Mixture (Gmb)
The ratio of the mass in air of a unit volume of a permeable material (including both permeable and impermeable voids normal to the material) at a stated temperature to the mass in air (of equal density) of an equal volume of gas-free distilled water at a stated temperature. This value is used to determine weight per unit volume of the compacted mixture. It is very important to measure Gmb as accurately as possible. Since it is used to convert weight measurements to volumes, any small errors in Gmb will be reflected in significant volume errors, which may go undetected.
The standard bulk specific gravity test is:
- AASHTO T 166: Bulk Specific Gravity of Compacted Bituminous Mixtures Using Saturated Surface-Dry Specimens
![]()
Theoretical Maximum Specific Gravity of Bituminous Paving Mixtures (Gmm)
The ratio of the mass of a given volume of voidless (Va = 0) HMA at a stated temperature (usually 25 °C) to a mass of an equal volume of gas-free distilled water at the same temperature. It is also called Rice Specific Gravity (after James Rice who developed the test procedure). Multiplying Gmm by the unit weight of water gives Theoretical Maximum Density (TMD).
The standard TMD test is:
- AASHTO T 209 and ASTM D 2041: Theoretical Maximum Specific Gravity and Density of Bituminous Paving Mixtures
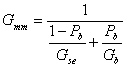 |
Voids (expressed as percentages)
Air Voids (Va)
The total volume of the small pockets of air between the coated aggregate particles throughout a compacted paving mixture, expressed as a percent of the bulk volume of the compacted paving mixture. The amount of air voids in a mixture is extremely important and closely related to stability and durability. For typical dense-graded mixes with 12.5 mm (0.5 inch) nominal maximum aggregate sizes air voids below about 3 percent result in an unstable mixture while air voids above about 8 percent result in a water-permeable mixture.
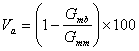 |
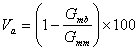 |
Voids in the Mineral Aggregate (VMA)
The volume of intergranular void space between the aggregate particles of a compacted paving mixture that includes the air voids and the effective asphalt content, expressed as a percent of the total volume of the specimen. When VMA is too low, there is not enough room in the mixture to add sufficient asphalt binder to adequately coat the individual aggregate particles. Also, mixes with a low VMA are more sensitive to small changes in asphalt binder content. Excessive VMA will cause an unacceptably low mixture stability (Roberts et al., 1996[1]). Generally, a minimum VMA is specified and a maximum VMA may or may not be specified.
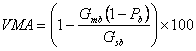 |
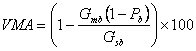 |
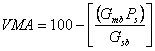 |
Voids Filled with Asphalt (VFA)
The portion of the voids in the mineral aggregate that contain asphalt binder. This represents the volume of the effective asphalt content. It can also be described as the percent of the volume of the VMA that is filled with asphalt cement. VFA is inversely related to air voids: as air voids decrease, the VFA increases.
Other Definitions
Effective Asphalt Content (Pbe)
The total asphalt binder content of the HMA less the portion of asphalt binder that is lost by absorption into the aggregate.
Volume of Absorbed Asphalt (Vba)
The volume of asphalt binder in the HMA that has been absorbed into the pore structure of the aggregate. It is the volume of the asphalt binder in the HMA that is not accounted for by the effective asphalt content.
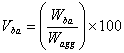 |
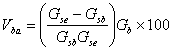 |
- Hot Mix Asphalt Materials, Mixture Design, and Construction. National Asphalt Pavement Association Education Foundation. Lanham, MD.↵
